Comprehensive Guide to Digital Accessibility and Assistive Technology
In today's digital landscape, digital accessibility ensures that all individuals, including those with disabilities, can effectively interact with digital content and services. Assistive technology encompasses tools and devices—such as screen readers, speech recognition software, and AI-powered applications—that aid users in navigating digital environments. Adherence to established accessibility standards is crucial for developers and organizations to create inclusive digital experiences that comply with legal and ethical guidelines. The integration of AI-powered accessibility solutions, like real-time captions and automated image descriptions, significantly enhances usability for individuals with diverse needs. Utilizing advanced assistive technology tools can bridge the gap between users and digital content, fostering independence and equal access. Regular accessibility testing is essential to identify and address potential barriers, ensuring that digital platforms remain usable and accessible to all.
General Accessibility & Digital Access
Core Concepts of Accessibility
Accessibility ensures that digital content is usable by all individuals, including those with disabilities. Web accessibility focuses on making websites and web applications accessible to people with diverse disabilities, such as visual, auditory, motor, and cognitive impairments. Digital accessibility extends this concept to all digital platforms, ensuring inclusivity across various devices and technologies.
Accessibility features are design elements that support users with disabilities, including alternative text for images, captions for videos, and adaptable navigation. Adherence to accessibility standards, such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), provides a framework for creating accessible web content. The Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI), part of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), develops these guidelines and offers resources to assist in their implementation.
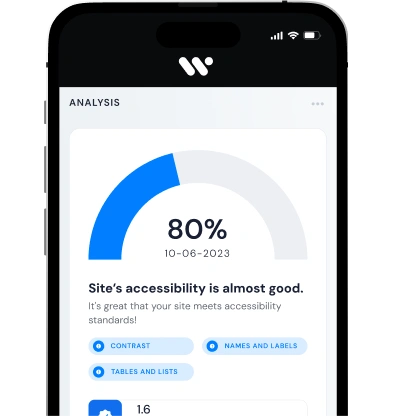
Tools like an accessibility checker help developers identify and address accessibility issues within their websites, promoting a more inclusive digital environment. The World Health Organization (WHO) emphasizes the importance of accessibility in digital health interventions, advocating for equitable access to health information and services for all individuals.
Understanding Assistive Technology and Its Impact
Assistive technology refers to devices and software designed to assist individuals with disabilities in performing tasks that might otherwise be challenging. Examples include screen readers, magnifiers, and speech recognition software These tools enable users to navigate websites and digital content more effectively, promoting inclusivity and independence
The Importance of Compatibility with Assistive Technology
Ensuring that websites and applications are compatible with assistive technology is vital for digital accessibility. This compatibility allows individuals with disabilities to navigate and interact with digital content effectively, aligning with accessibility standards and legal requirements.
Assistive Technology & Tools
General Assistive Technology
Assistive technology encompasses a broad range of tools and devices designed to enhance the functional capabilities of individuals with disabilities, promoting independence and improving quality of life. These technologies serve as reasonable accommodations in various settings, enabling disabled users to perform tasks that might otherwise be challenging.
Examples of Assistive Technology
- Mobility Aids: Devices such as wheelchairs and walkers that assist individuals with mobility impairments in moving around safely.
- Hearing Aids: Electronic devices that amplify sound for individuals with hearing loss, facilitating better communication.
- Screen Readers: Software applications that convert text on a screen into synthesized speech, aiding those with visual impairments in accessing digital content.
- Voice Recognition Software: Programs that allow users to control computers and input text using their voice, beneficial for individuals with mobility or dexterity challenges
The implementation of assistive technology as a reasonable accommodation is essential in creating inclusive environments, ensuring that individuals with disabilities have equal access to opportunities and resources.
AI-Powered Accessibility & Advanced Technology
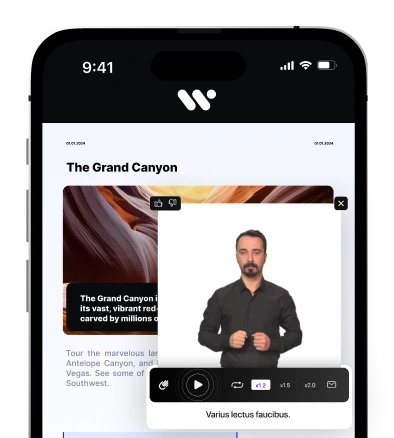
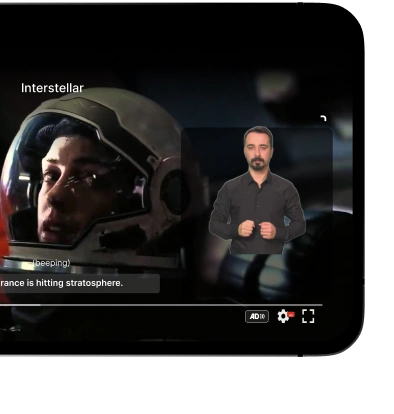
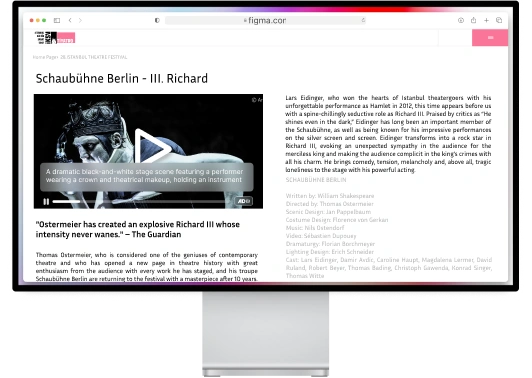
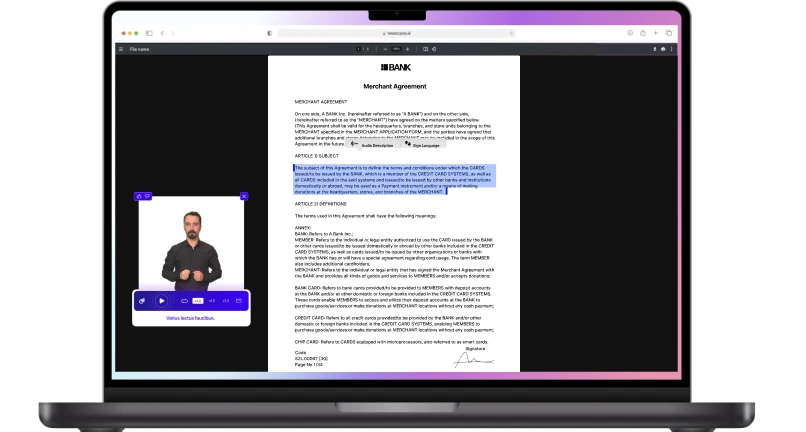
AI-driven accessibility tools are transforming how individuals with disabilities interact with digital content, making technology more inclusive. AI-powered accessibility tools use artificial intelligence to enhance the accessibility of websites and applications through features like real-time text-to-speech, voice commands, and automated image descriptions.
These advanced accessibility technologies are breaking down barriers for users with various impairments, including visual and hearing disabilities, by providing more intuitive ways to navigate digital environments. An AI accessibility service offers personalized solutions, adapting to individual needs and improving the overall user experience. By revolutionizing computer access, AI tools are creating a more inclusive digital world where people of all abilities can seamlessly interact with technology, empowering users to perform tasks that were once challenging.
AI-driven accessibility tools are revolutionizing how individuals with disabilities interact with digital platforms, enhancing usability and inclusivity. For instance, WeAccess.AI utilizes AI to automatically adjust website elements, ensuring compliance with accessibility standards without manual intervention.
Computer Access & Digital Interaction
Computer Access for People with Disabilities
Assistive technology plays a pivotal role in enabling individuals with disabilities to effectively interact with computers, enhancing their ability to operate digital devices and access information.
Assistive Technologies for Computer Access
- Alternative Input Devices: For users who face challenges with standard keyboards and mice, alternative input devices such as modified keyboards, eye-gaze trackers, and adaptive switches allow control of the computer through methods tailored to individual needs
- Screen Readers: Software like JAWS (Job Access With Speech) converts digital text into synthesized speech, enabling blind or visually impaired users to navigate and interact with digital content audibly
Operating a Computer with Assistive Technology
These assistive tools empower users to give the system commands, operate a computer, and access digital content effectively. Implementing appropriate accessibility software ensures that individuals with disabilities can utilize computers for communication, education, and employment, promoting independence and equal participation in digital spaces.
Visual Impairments & Screen Readers
Assistive Technologies for Blind and Visually Impaired Users
Screen Readers and Speech Recognition Software
Screen readers are essential tools for blind and visually impaired individuals, converting on-screen text into synthesized speech, enabling users to listen to digital content. Speech recognition software further enhances accessibility by allowing users to control their devices and input text through voice commands, offering an alternative to traditional typing. These tools allow blind or visually impaired users to fully interact with computers and mobile devices, fostering greater independence.
Braille Displays
Braille displays provide a tactile method of reading by translating on-screen text into Braille characters, enabling users to read digital content through touch. These devices, used alongside screen readers, create a comprehensive and interactive reading experience for individuals who are blind.
Advanced Object Recognition and Environmental Interaction
Advanced technology now includes systems that use AI to recognize objects, read text aloud, and provide descriptions of the user's environment. Such systems significantly improve mobility and interaction with surroundings, helping visually impaired individuals perform everyday tasks like reading signs, identifying objects, or navigating public spaces.
Mobile Applications for Visual Assistance
Several mobile applications provide real-time assistance, helping users read text, identify objects, and recognize faces in their environment. These apps use AI and computer vision technologies to enhance the user’s ability to engage with the world independently.
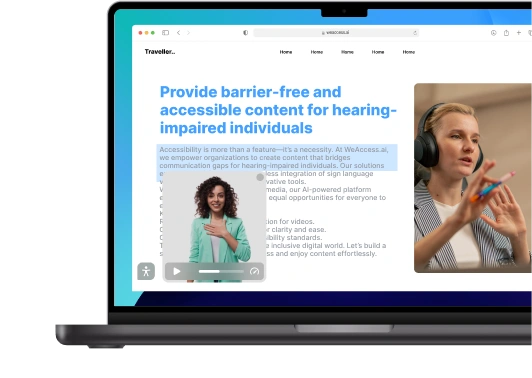
Hearing Disabilities & Assistive Technologies
Assistive Technologies for Deaf and Hard of Hearing Users
Advancements in assistive technologies have significantly improved communication and accessibility for individuals who are deaf or hard of hearing. These technologies encompass a range of devices and services designed to facilitate daily interactions and enhance the quality of life.
Hearing Aids
Hearing aids are electronic devices that amplify sound, aiding individuals with hearing loss in perceiving audio more clearly. They consist of microphones, amplifiers, and speakers, working together to enhance environmental sounds. Modern hearing aids are often programmable, allowing customization to the user's specific hearing needs
Closed Captioning
Closed captions display text on a screen, representing spoken words and non-verbal sounds, such as sound effects and music cues. They are commonly used in videos, television programs, and online content to provide accessible viewing experiences for individuals with hearing loss.
Alerting Devices
Alerting devices connect to doorbells, telephones, or alarms, emitting loud sounds or flashing lights to notify individuals with hearing loss of events like incoming calls or visitors. These devices enhance awareness of environmental cues that are typically conveyed through sound
Learning Disabilities & Cognitive Accessibility
Learning disabilities, such as dyslexia, affect an individual's ability to process information efficiently, impacting reading, writing, and sometimes even speech. For individuals with learning disabilities, assistive technology offers critical support by providing tools designed to overcome these challenges. Tools like text-to-speech software, word prediction software, and digital organizers help students and professionals manage their tasks more effectively.
Moreover, cognitive disabilities that affect memory, attention, or problem-solving abilities can be alleviated using apps that improve focus, enhance cognitive skills, and support structured learning.
Assistive Technologies for Learning and Cognitive Disabilities
Assistive technology (AT) encompasses tools and devices that aid individuals with learning and cognitive disabilities in performing tasks more effectively, thereby enhancing their educational experiences and daily activities.
Text-to-Speech and Speech-to-Text Software
Text-to-speech software converts written text into spoken words, assisting individuals with reading difficulties such as dyslexia by enabling auditory processing of information. Speech-to-text software allows users to dictate their thoughts, converting speech into written text, which supports those with writing challenges. These tools facilitate reading comprehension and writing fluency
Word Prediction and Spell Check Tools
Word prediction software suggests words as users type, reducing spelling errors and enhancing writing speed. Combined with spell check functionalities, these tools assist individuals in producing written content with greater accuracy and efficiency
Graphic Organizers
Graphic organizers are visual tools that help users structure information, aiding in planning and organizing thoughts for writing tasks. They assist in outlining ideas, making complex information more accessible and manageable
Mind Mapping Software
Mind mapping software enables users to create diagrams that represent words, ideas, or concepts, facilitating better understanding and organization of information. This tool supports brainstorming sessions and the development of complex ideas
AI-Powered Learning Tools
Recent advancements have introduced AI-powered tools that adapt to individual learning styles and needs, providing personalized educational experiences. These technologies offer tailored support, enhancing learning outcomes for students with cognitive disabilities.
Physical Disabilities & Mobility Aids
Assistive Technologies for Physical Accessibility and Mobility Support
Assistive technologies are pivotal in enhancing mobility and accessibility for individuals with physical disabilities, fostering greater independence and quality of life.
Wheelchairs and Mobility Aids
Wheelchairs, both manual and powered, are fundamental mobility aids that assist individuals in navigating various environments. Complementary devices such as walkers, canes, and crutches provide additional support, enabling users to maintain balance and move more freely. Innovations like exoskeletons further augment mobility, allowing users to stand and walk with assistance
Alternative Input Devices
For individuals with limited dexterity, alternative input devices facilitate interaction with computers and mobile devices. Pointer control devices, such as specialized mice or trackballs, enable precise cursor movement. Adaptive keyboards and on-screen keyboards offer customized typing solutions, accommodating various physical abilities. Eye-tracking systems allow users to control devices using eye movements, providing hands-free operation
Environmental Control Systems
Environmental control systems (ECS) empower users to manage aspects of their surroundings, including lighting, temperature, and entertainment systems, through accessible interfaces. These systems can be operated via voice commands, switches, or other adaptive devices, enhancing autonomy for individuals with mobility impairments
Assistive Technology Integration
The integration of assistive technologies into daily life is crucial for maximizing independence. It's essential to assess individual needs and select appropriate devices that align with personal capabilities and preferences. Collaboration with healthcare professionals and assistive technology specialists can aid in identifying suitable solutions and ensuring effective implementation.
Inclusive Design & Digital Inclusion
Embracing Inclusive Technology and Design
Inclusive technology and design focus on creating products and services accessible to all users, including those with diverse abilities. This approach aligns with the principles of digital inclusion, ensuring equitable access to digital resources.
Principles of Inclusive Design
Inclusive design involves understanding and addressing the needs of people with permanent, temporary, situational, or changing disabilities. Key principles include:
-
Recognize Exclusion: Identify and address biases that may exclude certain user groups.
-
Learn from Diversity: Embrace diverse perspectives to inform and enrich design processes.
-
Solve for One, Extend to Many: Design solutions that cater to individual needs, benefiting a broader audience
Usability Testing for Accessibility
Usability testing evaluates how effectively users can interact with a product or service. When focused on accessibility, it ensures that digital platforms are usable by individuals with various disabilities, including visual, auditory, motor, and cognitive impairments. This process involves assessing compliance with accessibility standards and identifying areas for improvement.
Resources for Inclusive Design
For comprehensive guidance on implementing inclusive design, consider exploring resources from organizations like the Design Council, which provides insights into designing for accessibility and inclusion.