Implementing web accessibility ensures equal access to digital content for individuals with disabilities, enhancing usability for all. Features like keyboard-only navigation and logical heading structures improve navigation for users with motor impairments and screen reader users.
Moreover, accessible websites often experience improved SEO rankings, as search engines favor sites with clear structures and descriptive alt texts. By prioritizing accessibility, businesses not only comply with legal standards but also expand their audience reach and demonstrate social responsibility.
What Is Web Accessibility and Why Is It Important?
Web accessibility ensures that websites, tools, and technologies are designed and developed so that people with disabilities can use them effectively. This includes individuals with visual, auditory, motor, and cognitive impairments, enabling them to perceive, understand, navigate, and interact with the web.
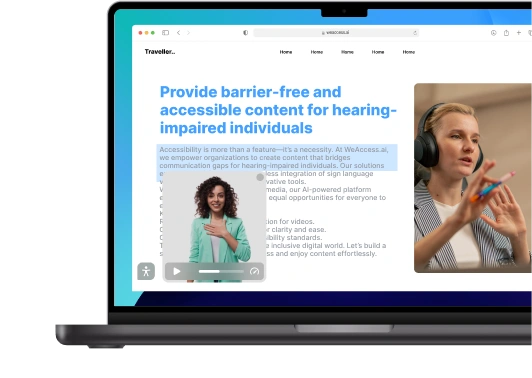
Digital accessibility is crucial for inclusivity, allowing everyone equal access to online information and services. It enhances usability for all users, improves search engine optimization (SEO), and ensures compliance with legal standards like the ADA and WCAG.
Accessibility is important not only for ethical and legal reasons but also for business. Accessible websites can reach a broader audience, including the aging population and individuals with temporary disabilities, thereby expanding market reach and demonstrating corporate social responsibility.
Defining Web Accessibility
Web accessibility means designing websites and digital tools so all users, including those with disabilities, can fully engage with online content. An accessible website allows individuals to navigate, understand, and interact with web content regardless of limitations such as vision, hearing, mobility, or cognitive challenges.
Accessibility also involves using proper HTML semantics, keyboard-friendly design, and descriptive alt text—making the internet more inclusive and user-friendly for everyone.
Why Accessibility Matters
The importance of website accessibility lies in its power to make the digital world usable for everyone, including over 1 billion people globally living with a disability. The importance of accessibility in web design goes beyond compliance—it creates a better, more inclusive user experience for all.
Inclusive Design: Who Benefits?
Inclusive design is the practice of creating websites and digital products that cater to a diverse audience, ensuring usability for all, including people with disabilities. By focusing on digital inclusion, designers ensure that no one is excluded based on ability, age, or technology access.
The benefits extend beyond users with disabilities to anyone facing temporary impairments, such as those with a broken arm, or those using mobile devices with limited functionality. This approach ensures equal access for a broader range of users, improving overall experience and engagement.
Accessibility for People with Disabilities
Accessibility for people with disabilities ensures that disabled users can navigate, engage with, and benefit from digital content just like anyone else. Websites that are accessible to people with disabilities use features like screen readers, alternative text, and keyboard-friendly navigation to provide equal access to all.
Designing with individuals with disabilities in mind promotes a more inclusive digital environment. By focusing on accessibility, businesses can create digital experiences that are welcoming and usable for everyone, fulfilling ethical obligations and enhancing user satisfaction.
Accessibility for All Users
Accessibility for all users ensures that everyone can use websites and digital products, regardless of their abilities. This includes users without disabilities as well, providing a better overall experience for all. Websites that support features like color blindness adjustments, hard of hearing accommodations (such as captions), and cognitive accessibility options make digital content more inclusive.
For users with visual impairment support, accessible websites provide screen reader compatibility and proper contrast ratios, ensuring that all individuals can access and interact with web content efficiently.
Key Benefits of Web Accessibility
The web accessibility benefits extend far beyond meeting legal requirements. Implementing accessible web design enhances user experience by making websites easier to navigate for everyone, including those with disabilities. This leads to improved benefits of website accessibility, such as increased traffic, higher engagement, and better user retention.
Moreover, businesses can reach a broader audience, improve SEO, and demonstrate social responsibility by making their websites benefits of accessible web available to all, including individuals with visual, auditory, or motor impairments. Accessibility also ensures compliance with global standards, minimizing legal risks.
Enhanced User Experience for All
Enhanced user experience is one of the most significant benefits of web accessibility. When websites are designed with accessibility in mind, they create a smoother overall user experience for everyone—regardless of ability. Features like easy navigation, readable fonts, and optimized color schemes improve the web experience, making it more enjoyable and intuitive.
By addressing the needs of users with various impairments, accessible websites ultimately deliver a better experience for all, improving satisfaction and engagement.
Expanded Audience Reach
Expanded audience reach is a major advantage of implementing web accessibility. By ensuring that websites are accessible to people with disabilities, businesses can tap into a wider audience, including individuals with visual, auditory, or motor impairments. This inclusivity opens up new customer segments, allowing brands to reach diverse groups that may have been previously excluded.
Making your site more accessible not only enhances user experience but also increases the potential to engage and convert a larger, more diverse audience.
Improved SEO Performance
Improved SEO performance is a key benefit of web accessibility. Accessible websites can help boost search engine optimization (SEO) by ensuring proper HTML structure, alt text for images, and descriptive links, all of which are favored by search engines. By making content easier to crawl and index, websites that prioritize accessibility tend to rank higher in search results.
Incorporating accessibility features, like clear navigation and mobile responsiveness, not only enhances usability but also improves visibility and organic traffic through better SEO.
Legal Compliance and Risk Reduction
Ensuring legal compliance through web accessibility is crucial for businesses, as it helps avoid potential accessibility lawsuits. Websites that adhere to ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act) standards and ADA requirements are less likely to face legal challenges, reducing risk and financial exposure. Meeting these standards ensures that websites are accessible to individuals with disabilities, providing equal access and preventing legal repercussions.
By proactively designing with accessibility in mind, businesses can demonstrate that their sites meet accessibility guidelines, fostering inclusivity while protecting themselves from costly legal issues.
Stronger Brand Reputation
A commitment to web accessibility can significantly enhance your brand reputation. By ensuring accessible content, businesses demonstrate a strong commitment to inclusivity and social responsibility. When content is accessible to all users, it not only improves the user experience but also positions the brand as ethical and forward-thinking.
Prioritizing accessibility shows that your brand cares about every customer, building trust and loyalty. Additionally, offering accessibility resources reinforces your brand's credibility, ultimately strengthening your relationship with a broader audience.
Accessibility Guidelines and Legal Requirements
Compliance with accessibility standards is essential for ensuring that websites are inclusive and usable for all users. The WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) set forth by the W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) provide a framework for creating accessible digital content. These guidelines focus on aspects like text alternatives for non-text content, navigation ease, and user-friendly interfaces.
In addition, legal frameworks like the ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act) and Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act mandate that websites meet certain accessibility requirements. Adhering to these guidelines not only ensures legal compliance but also fosters a more inclusive online environment for all users.
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG)
WCAG compliance is essential for ensuring that websites are accessible to individuals with disabilities. The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) provide detailed criteria for making web content more accessible, covering areas like text alternatives, navigation, and interactive elements. These guidelines are organized into four principles: Perceivable, Operable, Understandable, and Robust (POUR).
Adhering to WCAG standards helps businesses create digital content that meets the needs of a diverse audience, improving usability and fostering inclusivity while ensuring legal compliance.
ADA and Global Accessibility Laws
The ADA requirements (Americans with Disabilities Act) mandate that businesses provide equal access to their websites for people with disabilities. Under the ADA, websites must be accessible to individuals with visual, auditory, and motor impairments. Similarly, the Rehabilitation Act, specifically Section 508, requires that federal agencies' websites and digital content be accessible to people with disabilities. Globally, the European Accessibility Act aims to standardize accessibility across EU countries, ensuring that products and services, including websites, are accessible to people with disabilities. Complying with these laws not only avoids legal consequences but also demonstrates a commitment to inclusivity and accessibility.
Role of W3C and Standards Bodies
The W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) plays a pivotal role in setting standards for web accessibility through its W3C Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI). The WAI develops guidelines and resources, including the WCAG, to ensure that web content is accessible to all users, regardless of their abilities.
W3C’s efforts in establishing clear standards help designers and developers create inclusive digital experiences while promoting global web accessibility. By adhering to these standards, organizations contribute to a more equitable online environment.
Practical Approaches: How to Implement Web Accessibility Effectively
While understanding the principles and benefits of web accessibility is crucial, practical implementation ensures these advantages are realized. Incorporating accessibility requires a combination of design choices, coding best practices, and continuous testing.
Some practical steps include:
- Using semantic HTML elements correctly to convey structure and meaning.
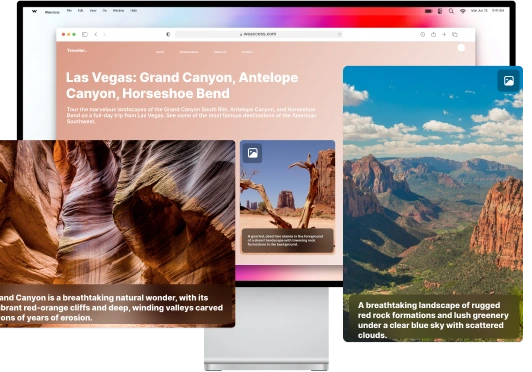
- Providing descriptive alt text for images, icons, and other visual content.
- Ensuring keyboard navigability for users unable to use a mouse.
- Designing with sufficient color contrast and text size for readability.
- Testing with assistive technologies like screen readers and keyboard-only navigation.
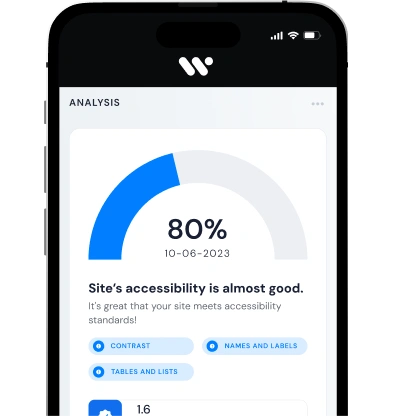
- Leveraging automated accessibility testing tools such as or Lighthouse to identify issues early.
This hands-on approach not only improves user experience but also positions your site for better SEO and legal compliance.
Local and Regional Accessibility Regulations: A Closer Look
In addition to global standards, local laws often impose specific requirements. For example, in Turkey, the recent Digital Accessibility Law mandates public and private sector websites to meet defined accessibility standards, ensuring digital inclusion for all citizens.
Understanding and complying with these local regulations alongside international guidelines like WCAG and ADA ensures comprehensive legal protection and market relevance.
The Connection Between Accessibility and Technical Performance
Web accessibility and site performance are intertwined. Accessible websites tend to have cleaner code, faster load times, and better mobile responsiveness, all factors that contribute to higher search engine rankings.
Optimizing images, minimizing JavaScript, and adopting responsive design techniques enhance both accessibility and technical SEO, delivering superior user experiences across devices.
Enhancing User Experience Through Accessibility: Real-World Impact
Accessible design improves overall UX by addressing diverse user needs:
- Clear navigation helps all users find information quickly.
- Readable fonts and well-organized layouts reduce cognitive load.
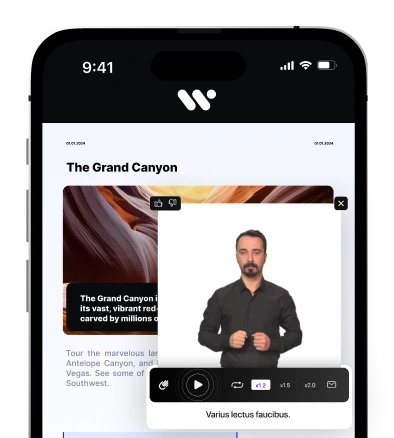
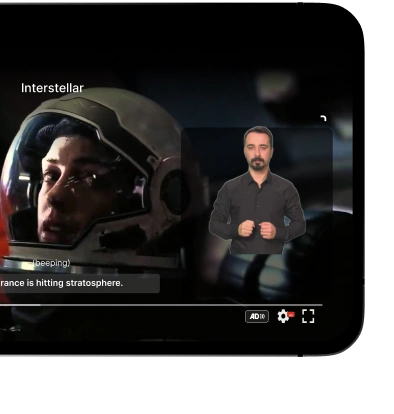
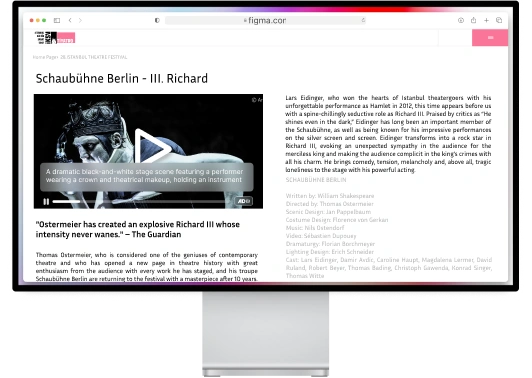
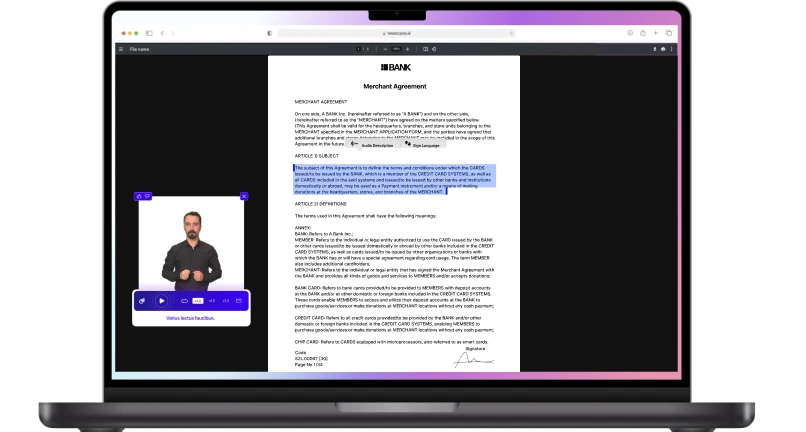
- Captioned videos and transcripts make multimedia content usable for everyone.
- Consistent and predictable interfaces build user confidence.
Empirical studies show that investing in accessibility can increase customer satisfaction, reduce bounce rates, and foster long-term loyalty.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Web Accessibility
Q1: How can I test if my website is accessible?
A1: Use tools like or Google Lighthouse. Also, manual testing with keyboard navigation and screen readers is essential.
Q2: Does making my website accessible help SEO?
A2: Yes. Accessible websites often rank better because search engines prefer well-structured, easily crawlable content.
Q3: Is accessibility compliance mandatory?
A3: Depending on your jurisdiction, legal requirements vary. However, accessibility is increasingly enforced globally.
Q4: How long does it take to make a website accessible?
A4: Time depends on site complexity. Incorporating accessibility from the start is ideal; retrofitting can be more time-consuming.